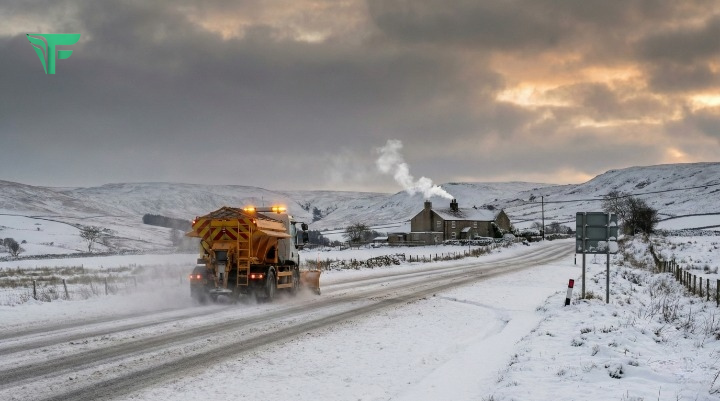
The polar vortex collapse forecast has meteorologists closely watching Arctic conditions as winter approaches. Recent stratospheric warming events suggest we could see dramatic temperature swings and severe cold outbreaks across North America in the coming months.
Understanding the Polar Vortex
The polar vortex is a large area of low pressure and cold air that sits over both poles. Think of it as a spinning wheel of frigid air that typically stays contained in the Arctic region. When this system remains strong and stable, it keeps the coldest air locked up north, away from populated areas.
However, when the polar vortex weakens, everything changes. The cold air that was once trapped near the North Pole begins to spill southward, bringing extreme cold weather to places that don’t normally experience such harsh conditions.
What Causes Polar Vortex Disruption?
Several factors can disrupt the polar vortex:
- Sudden stratospheric warming events that heat the upper atmosphere
- Changes in atmospheric pressure patterns
- Solar activity and radiation variations
- Ocean temperature fluctuations
- Jet stream instability
When these disruptions occur, the normally tight circulation of cold air around the pole becomes wobbly and stretched, allowing Arctic air masses to break free and travel south.
How Polar Vortex Collapse Works
A polar vortex split doesn’t happen overnight. The process typically unfolds over several weeks, starting in the stratosphere before making its way down to surface weather patterns.
The Three-Stage Process
Stage 1: Stratospheric Disruption
High up in the atmosphere, temperatures begin rising rapidly. This sudden stratospheric warming can increase temperatures by 50-100 degrees Fahrenheit in just a few days.
Stage 2: Weakening and Stretching
The circular pattern of the polar vortex becomes distorted. Instead of one strong, centered circulation, it may split into two or more weaker pieces.
Stage 3: Surface Impact
The effects finally reach ground level, bringing Arctic air outbreaks and dramatic temperature drops to lower latitudes.
Current Winter Weather Predictions
Meteorologists are monitoring several key indicators that suggest increased polar vortex activity this winter. Computer models show above-normal chances for sudden stratospheric warming events between December and February.
Key Forecast Elements
The long-range forecast indicates:
- Higher probability of polar vortex disruption events
- Increased likelihood of extreme cold snaps in January and February
- Greater temperature variability throughout the winter season
- Potential for record-breaking cold temperatures in some regions
NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center has issued preliminary outlooks suggesting that parts of the northern United States could experience below-normal temperatures during peak winter months, largely due to expected polar vortex fluctuations.
Timing Predictions
Based on current atmospheric patterns and historical data, the most likely timeframe for significant polar vortex collapse events appears to be:
- Late December to early January: Initial weakening phases
- Mid-January to February: Peak disruption period
- March: Potential for late-season cold outbreaks
Signs of Polar Vortex Disruption
Weather enthusiasts and professionals watch for specific indicators that suggest the polar vortex is becoming unstable. Understanding these signs can help predict when severe winter weather might be heading south.
Atmospheric Indicators
Temperature Anomalies in the Stratosphere
Scientists monitor temperatures 10-30 miles above Earth’s surface. When these temperatures rise rapidly over the Arctic, it’s often the first sign of polar vortex troubles ahead.
Wind Speed Changes
The polar vortex is characterized by strong winds circling the pole. When these winds slow down significantly or even reverse direction, it indicates the system is weakening.
Pressure Pattern Shifts
Changes in atmospheric pressure over the Arctic and surrounding regions can signal that the polar vortex is losing its grip on the cold air.
Observable Weather Patterns
People don’t need specialized equipment to notice some signs of polar vortex disruption:
- Unusual weather patterns in Alaska and northern Canada
- Temperature swings in northern Europe and Siberia
- Changes in storm tracks across the North Atlantic
- Shifts in the jet stream position
Regional Impact Across North America
When the polar vortex collapses, different regions experience varying impacts. Understanding these regional differences helps people prepare for what might be coming their way.
Great Lakes Region
The Great Lakes area often bears the brunt of Arctic blast events. Cities like Chicago, Detroit, and Buffalo frequently see:
- Temperature drops of 40-60 degrees in 24-48 hours
- Enhanced lake-effect snow due to temperature contrasts
- Wind chills reaching dangerous levels
- Increased heating demands and energy usage
Northeast Corridor
From Boston to Washington, D.C., polar vortex events can bring:
- Sudden freezing of normally mild coastal areas
- Increased risk of burst pipes and infrastructure damage
- Flight delays and cancellations at major airports
- School and business closures due to extreme conditions
Midwest and Plains States
The broad, flat terrain of the Midwest offers little protection from Arctic air masses:
- Widespread temperature records often fall during these events
- Agricultural impacts on livestock and winter crops
- Increased risk of frostbite and hypothermia
- Strain on electrical grids due to heating demands
Southern States
Even regions unaccustomed to severe cold can feel the impact:
- Rare snowfall in normally warm climates
- Infrastructure not designed for extreme cold faces challenges
- Economic disruptions in areas unprepared for winter weather
- Increased risk to homeless populations and outdoor workers
Preparing for Sudden Stratospheric Warming
Sudden stratospheric warming serves as an early warning system for potential polar vortex collapse events. This phenomenon occurs when the stratosphere over the Arctic rapidly heats up, weakening the polar vortex below.
Understanding the Timeline
The connection between stratospheric warming and surface weather isn’t immediate:
- Week 1-2: Warming occurs in the stratosphere
- Week 3-4: Effects begin propagating downward
- Week 4-8: Surface weather impacts become apparent
This lag time gives meteorologists and the public several weeks to prepare for potential extreme weather events.
Monitoring Resources
Several organizations provide regular updates on polar vortex conditions:
- National Weather Service: Issues winter weather outlooks and warnings
- NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center: Provides monthly and seasonal forecasts
- European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts: Offers global modeling data
- Universities and research institutions: Publish detailed analysis and predictions
Climate Change and Arctic Weather Patterns
The relationship between climate change and polar vortex behavior remains an active area of research. Some scientists suggest that Arctic warming may be making polar vortex disruptions more frequent and intense.
The Arctic Warming Connection
As the Arctic warms faster than other regions, several changes occur:
- Reduced temperature difference between the Arctic and lower latitudes
- Weakening of the jet stream, which helps maintain the polar vortex
- Changes in atmospheric circulation patterns
- Increased variability in winter weather patterns
Conflicting Research
Not all scientists agree on how climate change affects the polar vortex:
Some studies suggest:
- More frequent polar vortex disruptions
- Longer-lasting cold outbreaks when they do occur
- Increased weather variability and unpredictability
Other research indicates:
- No clear long-term trend in polar vortex behavior
- Natural variability explains most observed changes
- Limited evidence for increased disruption frequency
Also Read: https://flyermagazines.co.uk/everton-vs-brentford/
Ongoing Research
Scientists continue studying these connections through:
- Advanced computer modeling of atmospheric circulation
- Analysis of historical weather data and trends
- Satellite monitoring of Arctic conditions
- International research collaborations
Long-Range Weather Forecasting
Predicting polar vortex events challenges even the most sophisticated forecasting systems. Seasonal weather prediction requires understanding complex interactions between ocean, atmosphere, and ice conditions.
Forecast Limitations
Several factors make long-range winter weather forecasting difficult:
- Chaos theory: Small changes in initial conditions can lead to vastly different outcomes
- Model limitations: Computer models struggle with complex atmospheric interactions
- Data quality: Limited observations in remote Arctic regions
- Natural variability: Weather patterns naturally fluctuate over multiple timescales
Forecast Improvements
Recent advances have enhanced polar vortex prediction:
- Better stratospheric monitoring systems
- Improved computer models with higher resolution
- Enhanced understanding of ocean-atmosphere interactions
- Machine learning applications in weather prediction
Probabilistic Forecasting
Modern forecasts focus on probabilities rather than specific predictions:
- “Above normal chance” for cold weather outbreaks
- Confidence intervals around temperature predictions
- Ensemble forecasting using multiple model runs
- Risk-based communication for decision-makers
Historical Polar Vortex Events
Looking at past polar vortex collapses helps meteorologists understand what might happen in future events. Several memorable episodes provide insight into the potential impacts of these phenomena.
The 2014 Polar Vortex
One of the most memorable recent events occurred in January 2014:
- Temperatures dropped to -37°F in Chicago
- Atlanta, Georgia saw rare ice storms and snow
- Widespread school and business closures across the Midwest
- Economic losses exceeded $5 billion
This event demonstrated how Arctic air outbreaks could affect regions far south of their normal range.
The 2019 Extreme Cold Event
Another significant polar vortex split occurred in late January 2019:
- Record-breaking cold temperatures across the Midwest
- Chicago experienced temperatures colder than Antarctica
- Mail delivery suspended in multiple states
- Frostbite warnings issued for exposed skin
The 2021 Texas Freeze
While not a classic polar vortex event, the February 2021 cold snap in Texas showed how extreme cold weather could overwhelm unprepared infrastructure:
- Widespread power outages affecting millions
- Water system failures across the state
- Economic damages exceeding $100 billion
- Multiple fatalities related to cold exposure and carbon monoxide poisoning
Expert Predictions for This Season
Current polar vortex collapse forecast models suggest increased activity this winter season. Leading meteorologists and climate scientists are monitoring several key indicators that point toward potential disruptions.
Key Forecast Factors
Ocean Temperature Patterns
Sea surface temperatures in the North Atlantic and Pacific can influence atmospheric circulation patterns. Current conditions show:
- Neutral to weak La Niña conditions in the Pacific
- Above-normal temperatures in parts of the North Atlantic
- Arctic sea ice extent below long-term averages
Stratospheric Conditions
Early season measurements of stratospheric temperatures and wind patterns indicate:
- Normal to slightly below-normal polar vortex strength
- Increased potential for sudden warming events
- Historical analogs suggesting active winter season
Regional Outlook
Northern Plains and Upper Midwest
These regions show the highest probability for extreme cold events:
- 60-70% chance of below-normal temperatures during peak winter
- Increased likelihood of prolonged cold snaps
- Higher risk of infrastructure challenges
Northeast and Mid-Atlantic
Moderate probability for Arctic air intrusions:
- 55-60% chance of significant cold events
- Potential for rapid temperature changes
- Increased heating degree day requirements
Southeast and Gulf Coast
Lower but non-zero probability for unusual cold:
- 30-40% chance of notable cold outbreaks
- Risk of agricultural and infrastructure impacts
- Rare snow and ice possibilities
Understanding the polar vortex collapse forecast helps everyone prepare for what could be a challenging winter season. While predicting exact timing and intensity remains difficult, current atmospheric patterns suggest increased chances for extreme winter weather events across North America. Stay informed through reliable weather sources, prepare emergency supplies, and remember that Arctic weather patterns can change rapidly. Monitor local forecasts closely as the season progresses, and don’t hesitate to take protective measures when severe cold warnings are issued for your area.
Ready for winter? Share your preparation tips in the comments below and subscribe to our weather updates for the latest polar vortex tracking information.