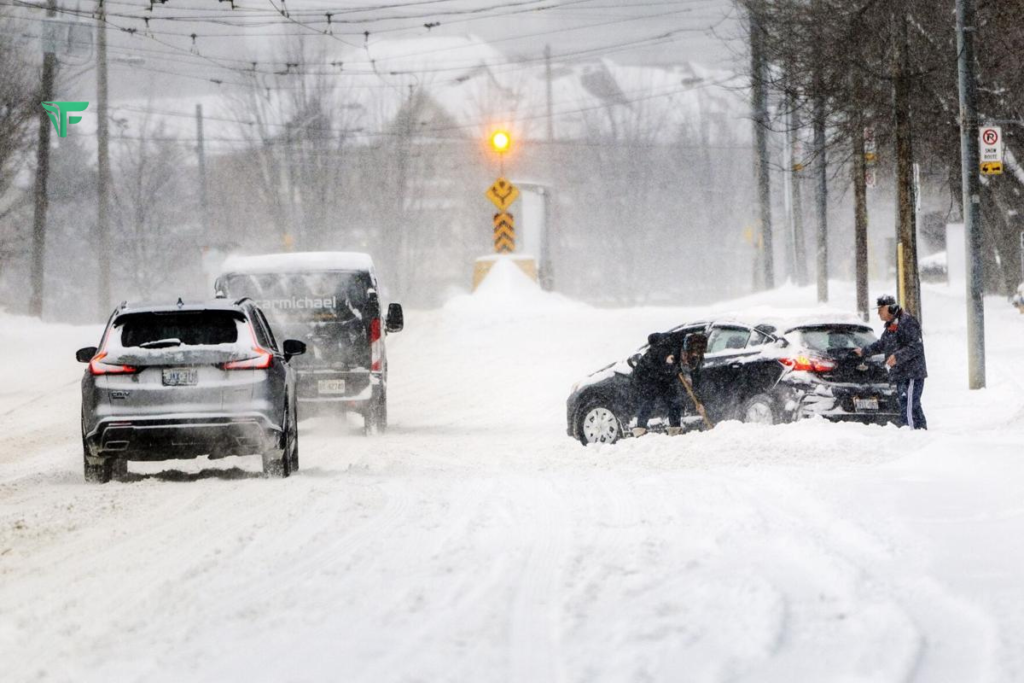
When winter approaches, staying informed about the snow storm weather forecast becomes crucial for everyone’s safety and daily planning. Understanding winter weather predictions can mean the difference between being caught off guard and being properly prepared for severe weather conditions.
Understanding Snow Storm Weather Forecasting
Snow storm weather forecasting involves complex meteorological analysis that combines multiple data sources to predict when, where, and how much snow will fall. Modern weather forecasting has become incredibly sophisticated, allowing meteorologists to provide detailed predictions up to seven days in advance with reasonable accuracy.
The foundation of any reliable snow storm weather forecast begins with atmospheric pressure systems, temperature gradients, and moisture content in the air. These three elements work together to create the perfect conditions for snow formation and accumulation.
What Makes Snow Storm Prediction Challenging
Predicting snowstorms presents unique challenges compared to other weather events. Small changes in temperature can dramatically affect whether precipitation falls as snow, sleet, or rain. Even a difference of just two degrees Fahrenheit can completely change the outcome of a storm system.
Key factors that complicate snow forecasting include:
- Temperature variations at different altitudes
- Wind speed and direction changes
- Ground temperature conditions
- Humidity levels throughout the atmosphere
- Interaction between multiple weather systems
Key Elements of Winter Weather Predictions
Successful winter weather predictions rely on several critical components that meteorologists carefully monitor and analyze. Understanding these elements helps you better interpret weather forecasts and make informed decisions about your daily activities.
Temperature Profiles
Temperature plays the most important role in snow storm weather forecast accuracy. Meteorologists examine temperature readings at various atmospheric levels, not just surface temperatures. The entire temperature profile from ground level to 30,000 feet determines whether precipitation will be snow, rain, or a mix of both.
Surface temperatures below 32°F typically ensure snow accumulation, but upper-level temperatures also matter significantly. Warm air layers aloft can cause snow to melt and refreeze, creating dangerous ice storms instead of fluffy snow.
Precipitation Timing and Duration
The timing and duration of snowfall greatly impact total accumulation amounts. Light snow over many hours often produces more total accumulation than heavy snow for short periods. Winter weather predictions must account for when snow will start, peak intensity periods, and when conditions will improve.
Storm duration affects preparation time available to residents and emergency services. Longer-duration storms typically cause more significant travel disruptions and require extended preparation periods.
Wind Conditions and Blizzard Criteria
Wind speed transforms ordinary snowfall into dangerous blizzard conditions. The National Weather Service defines blizzard conditions as sustained winds of 35 mph or greater with considerable falling or blowing snow that reduces visibility to less than one-quarter mile for three hours or more.
High winds during snowstorms create several additional hazards:
- Reduced visibility making travel extremely dangerous
- Wind chill effects that increase frostbite and hypothermia risks
- Uneven snow distribution with dangerous drifting
- Increased likelihood of power outages from downed lines
How Meteorologists Predict Snowstorms
Modern snow storm weather forecasting combines traditional meteorological knowledge with advanced computer modeling systems. Professional meteorologists use sophisticated tools and techniques to analyze atmospheric conditions and predict winter weather patterns with increasing accuracy.
Computer Weather Models
Numerical weather prediction models form the backbone of modern forecasting. These complex computer programs process millions of data points from weather stations, satellites, and atmospheric sensors worldwide. The most commonly used models for snow prediction include:
Global Forecast System (GFS): Operated by the National Weather Service, this model provides forecasts up to 16 days in advance with decreasing accuracy over time.
European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF): Often considered the most accurate global model, particularly for medium-range forecasts 3-7 days out.
North American Mesoscale Model (NAM): Focuses on detailed short-range forecasts for North America with higher resolution than global models.
Data Collection Networks
Accurate snow storm weather forecasts depend on comprehensive data collection from multiple sources. Weather stations across the country continuously monitor temperature, humidity, wind speed, and atmospheric pressure. Upper-air observations from weather balloons provide crucial information about atmospheric conditions at various altitudes.
Satellite imagery offers real-time views of developing storm systems, cloud patterns, and moisture content. Doppler radar systems can detect precipitation type and intensity, allowing meteorologists to track storm movement and evolution in real-time.
Ensemble Forecasting
To account for uncertainty in weather predictions, meteorologists use ensemble forecasting techniques. This approach runs multiple slightly different computer model simulations to generate a range of possible outcomes. Ensemble forecasting helps identify forecast confidence levels and potential variations in storm tracks or intensity.
Reading Winter Weather Alerts and Warnings
Understanding different types of winter weather alerts helps you respond appropriately to threatening conditions. The National Weather Service issues various levels of warnings based on expected storm severity and potential impacts.
Winter Weather Advisory
A Winter Weather Advisory indicates that snow, sleet, or freezing rain will cause significant inconveniences and may be hazardous. These conditions typically involve:
- Snow accumulations of 2-5 inches in 12 hours
- Sleet accumulations up to half an inch
- Freezing rain with minimal ice accumulation
During advisory conditions, exercise caution while driving and allow extra time for travel. Road conditions may become slippery, but major travel disruptions are unlikely.
Winter Storm Watch
Winter Storm Watches are issued when there’s potential for significant winter weather within 48 hours. This alert means conditions are favorable for a major snow storm, but the timing, track, or intensity remains uncertain.
Use watch periods to prepare emergency supplies, review travel plans, and stay updated on forecast changes. Watches often get upgraded to warnings as storm details become clearer.
Winter Storm Warning
Winter Storm Warnings indicate that dangerous winter weather is imminent or already occurring. Warning criteria typically include:
- Snow accumulations of 6 inches or more in 12 hours
- Ice accumulations of one-quarter inch or more
- A combination of snow and ice that will create hazardous conditions
Take winter storm warnings seriously and avoid unnecessary travel. These conditions can quickly become life-threatening, especially if you become stranded.
Blizzard Warning
Blizzard Warnings represent the most serious winter weather alert. These warnings are issued when sustained winds of 35 mph or greater combine with considerable falling or blowing snow, reducing visibility to near zero for extended periods.
Blizzard conditions can develop rapidly and create extremely dangerous situations. Avoid all travel during blizzard warnings and ensure you have adequate emergency supplies if power outages occur.
Technology Behind Accurate Snow Predictions
Advanced technology continues to improve snow storm weather forecast accuracy through better data collection, processing power, and analytical techniques. Understanding these technological improvements helps explain why modern forecasts are more reliable than ever before.
Doppler Radar Advancements
Next-generation Doppler radar systems provide detailed information about precipitation type, intensity, and movement. Dual-polarization radar technology can distinguish between snow, rain, sleet, and hail by analyzing how precipitation particles reflect radar signals.
These radar improvements allow meteorologists to track storm evolution in real-time and provide more accurate nowcasting – forecasts for the immediate future up to six hours ahead.
Satellite Technology
Modern weather satellites equipped with advanced sensors monitor atmospheric conditions from space 24 hours a day. Geostationary satellites provide continuous monitoring of the same geographic area, while polar-orbiting satellites offer detailed global coverage twice daily.
Satellite data helps meteorologists track storm development, measure cloud top temperatures, and estimate precipitation amounts over large areas where ground-based observations are sparse.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Machine learning and artificial intelligence are increasingly being integrated into weather forecasting systems. These technologies can identify patterns in massive datasets that human forecasters might miss and help correct systematic model biases.
AI systems can also process multiple data sources simultaneously to provide more accurate short-term forecasts and better uncertainty estimates.
Regional Differences in Snow Storm Patterns
Snow storm weather forecast accuracy and storm characteristics vary significantly across different geographic regions. Understanding these regional differences helps you better prepare for winter weather specific to your area.
Great Lakes Snow Effect
The Great Lakes region experiences unique snow patterns called lake-effect snow. When cold air masses move across relatively warm lake waters, they pick up moisture and create intense, localized snowfall bands.
Lake-effect snow can produce snowfall rates of 2-4 inches per hour in narrow bands while areas just miles away remain clear. These storms are particularly challenging to forecast because small changes in wind direction can dramatically shift snow band locations.
Nor’easter Storms
The northeastern United States frequently experiences powerful coastal storms called nor’easters. These storms develop when cold arctic air meets warm, moist air from the Atlantic Ocean, creating intense low-pressure systems that move up the coast.
Nor’easters can produce heavy snow, strong winds, and coastal flooding simultaneously. The exact storm track determines which areas receive the heaviest snow, making precise forecasting critical for preparation efforts.
Rocky Mountain Snow
Mountain regions present unique forecasting challenges due to complex terrain effects. Elevation changes, wind patterns, and valley orientations all influence snow accumulation patterns.
Orographic lifting causes air masses to rise and cool as they encounter mountain slopes, enhancing snowfall on windward sides while creating snow shadows in protected valleys. Temperature inversions common in mountain areas can also affect precipitation type at different elevations.
Plains Blizzards
The Great Plains region experiences some of the most severe blizzard conditions in North America. Flat terrain allows arctic air masses to move rapidly southward while providing little protection from strong winds.
Plains blizzards often feature relatively modest snowfall amounts but extremely dangerous wind-driven conditions. Ground blizzards can develop even without falling snow when strong winds lift existing snow cover.
Essential Snow Storm Preparation Tips
Proper preparation before a snow storm weather forecast calls for severe conditions can prevent emergencies and ensure your family’s safety throughout winter weather events.
Home Preparation Checklist
Preparing your home before winter storms arrive involves several important steps that can prevent damage and maintain comfort during extended power outages or isolation periods.
Heating System Maintenance: Service your heating system before winter begins. Clean or replace filters, check fuel supplies, and ensure backup heating sources are ready. If you use a fireplace, have the chimney cleaned and inspected.
Insulation and Weather Sealing: Improve your home’s energy efficiency by sealing air leaks around windows, doors, and other openings. Proper insulation reduces heating costs and helps maintain comfortable temperatures during storms.
Also Read: https://flyermagazines.co.uk/storm-goretti/
Pipe Protection: Insulate pipes in unheated areas and know how to shut off your main water supply. Frozen pipes can burst and cause expensive damage. Keep faucets slightly dripping during extreme cold to prevent freezing.
Generator Safety: If you have a portable generator, ensure it’s properly maintained and never operate it inside your home or garage. Carbon monoxide poisoning is a serious risk that claims lives every winter.
Communication and Information
Staying informed during winter storms requires reliable communication methods and information sources. Develop multiple ways to receive weather updates and emergency information.
Battery-Powered Radio: Keep a battery-powered or hand-crank radio to receive emergency broadcasts if power goes out. NOAA Weather Radio provides continuous weather updates and emergency alerts.
Cell Phone Preparation: Keep cell phones fully charged before storms arrive and consider portable battery packs for extended power outages. Download weather apps that work offline or with limited connectivity.
Emergency Contacts: Maintain a written list of important phone numbers including utility companies, emergency services, family members, and neighbors. Cell phone contact lists may be inaccessible during power outages.
Vehicle Winter Preparation
Preparing your vehicle for winter weather ensures reliable transportation and safety during snow storm conditions.
Winter Tires or Chains: Install winter tires or carry approved tire chains if required in your area. All-season tires perform poorly in snow and ice compared to dedicated winter tires.
Emergency Kit: Keep a winter emergency kit in your vehicle including blankets, food, water, flashlight, first aid supplies, jumper cables, shovel, ice scraper, and sand or cat litter for traction.
Fuel and Maintenance: Keep your gas tank at least half full during winter months. Check battery condition, antifreeze levels, and wiper blades before winter weather arrives.
Emergency Supplies for Winter Weather
Maintaining adequate emergency supplies ensures your family can safely weather extended winter storms without outside assistance.
Food and Water Storage
Store enough non-perishable food and water for each family member for at least three days, though a week’s supply is preferable for severe winter weather areas.
Water Requirements: Plan for one gallon of water per person per day for drinking, cooking, and hygiene. Store water in clean containers and rotate supplies every six months.
Food Selection: Choose foods that require no cooking or refrigeration such as canned goods, dried fruits, nuts, granola bars, and peanut butter. Include a manual can opener and disposable plates and utensils.
Special Dietary Needs: Don’t forget infant formula, pet food, and medications that require refrigeration. Consider family members with special dietary restrictions or medical conditions.
Heating and Lighting
Alternative heating and lighting sources become critical during extended power outages caused by winter storms.
Flashlights and Batteries: Maintain several flashlights with fresh batteries rather than relying solely on candles which present fire hazards. LED flashlights provide longer battery life and brighter illumination.
Alternative Heating: Safe alternative heating options include kerosene heaters, wood-burning stoves, or fireplaces with adequate fuel supplies. Never use camping stoves, charcoal grills, or generators indoors due to carbon monoxide risks.
Warm Clothing and Bedding: Extra blankets, sleeping bags, and warm clothing help maintain body heat when indoor temperatures drop. Layer clothing for maximum warmth and have extra socks and gloves available.
First Aid and Medications
Medical emergencies become more serious during winter storms when emergency services may be delayed or unavailable.
First Aid Kit: Maintain a well-stocked first aid kit including bandages, antiseptic, pain relievers, thermometer, and any prescription medications family members need.
Prescription Medications: Keep at least a seven-day supply of all prescription medications and rotate supplies before expiration dates. Include copies of prescriptions and medical information.
Emergency Medical Information: Maintain current medical information for all family members including allergies, medical conditions, and emergency contacts for healthcare providers.
Travel Safety During Snow Storms
When snow storm weather forecasts predict dangerous conditions, the safest choice is avoiding travel altogether. However, if travel becomes necessary, proper preparation and precautions can prevent emergencies.
Pre-Travel Planning
Before departing during winter weather, thoroughly plan your route and inform others of your travel plans.
Route Selection: Choose main highways that receive priority snow removal over back roads. Familiarize yourself with alternate routes in case primary roads become impassable.
Timing Considerations: Travel during daylight hours when possible and avoid rush hour periods when traffic congestion increases accident risks. Monitor current road conditions through state transportation websites.
Communication Plan: Inform family or friends of your departure time, planned route, and expected arrival time. Agree on check-in times and what actions to take if you don’t arrive as scheduled.
Driving Techniques for Snow and Ice
Safe winter driving requires different techniques and increased caution compared to normal conditions.
Speed and Following Distance: Reduce speed significantly below posted limits and increase following distance to at least eight seconds behind other vehicles. Stopping distances increase dramatically on snow and ice.
Acceleration and Braking: Apply gas and brakes gently to avoid wheel spin or skidding. If your vehicle has anti-lock brakes, apply firm steady pressure and let the system work rather than pumping the brakes.
Steering Control: Make smooth, gradual steering movements and avoid sudden direction changes that can cause loss of control. If you start to skid, steer in the direction you want to go and avoid overcorrecting.
Vehicle Emergency Procedures
Despite careful preparation, vehicle emergencies can still occur during winter travel. Knowing proper emergency procedures can save lives.
If You Become Stuck: Stay with your vehicle unless help is clearly visible nearby. Your car provides shelter and makes you more visible to rescue crews than wandering in a storm.
Conserving Fuel and Staying Warm: Run the engine and heater for about 10 minutes each hour to conserve fuel while staying warm. Clear snow from the exhaust pipe to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
Signaling for Help: Use hazard lights, bright cloth tied to the antenna, or raising the hood to signal distress. In modern vehicles, cell phone emergency services can often locate you even without exact coordinates.
Post-Storm Recovery and Safety
After winter storms pass, recovery efforts present their own safety challenges that require careful attention and planning.
Snow Removal Safety
Clearing snow from driveways, sidewalks, and roofs can be physically demanding and potentially dangerous work.
Shoveling Techniques: Use proper lifting techniques by bending your knees and lifting with your legs rather than your back. Take frequent breaks and push snow rather than lifting when possible.
Heart Attack Prevention: Cold weather and physical exertion significantly increase heart attack risks, especially for people with existing heart conditions or those who don’t exercise regularly. Stop immediately if you experience chest pain or breathing difficulties.
Roof Snow Load: Monitor snow accumulation on roofs and arrange for professional removal if loads become dangerous. Ice dams can also cause water damage when snow melts and refreezes.
Power Outage Recovery
Extended power outages often follow severe winter storms, requiring careful attention to safety during restoration periods.
Electrical Safety: Have qualified electricians inspect electrical systems damaged by storms before restoring power. Use flashlights rather than candles to inspect damage and avoid electrocution hazards from downed power lines.
Carbon Monoxide Awareness: Continue monitoring for carbon monoxide hazards from generators, heating systems, or blocked vents even after power restoration. Symptoms include headache, dizziness, and nausea.
Food Safety: Discard perishable food that has been above 40°F for more than two hours. When in doubt, throw it out rather than risk foodborne illness.
Community Recovery Assistance
Winter storm recovery often involves community-wide efforts to restore normal operations and help neighbors in need.
Checking on Neighbors: Elderly neighbors or those with medical conditions may need assistance during recovery periods. Offer help with snow removal, transportation, or emergency supplies.
Emergency Services: Be patient with emergency services and utility crews working to restore normal operations. Report downed power lines, gas leaks, or other hazards immediately but avoid attempting repairs yourself.
Volunteer Opportunities: Many communities organize volunteer efforts to help with storm cleanup and recovery. Contact local emergency management or volunteer organizations to find ways to help.
Staying informed about snow storm weather forecasts and preparing adequately for winter weather protects your family and helps your community recover more quickly from severe storms. Modern forecasting technology provides excellent advance warning, but personal preparation and safe decision-making remain the most important factors in winter weather safety. Monitor trusted weather sources regularly during winter months and never hesitate to take protective action when dangerous conditions are predicted.
Ready to improve your winter weather preparedness? Share this guide with friends and family, bookmark reliable weather forecast sources, and start building your emergency supply kit today. Your preparation efforts could save lives when the next major snow storm arrives.